alumni comments

"
"
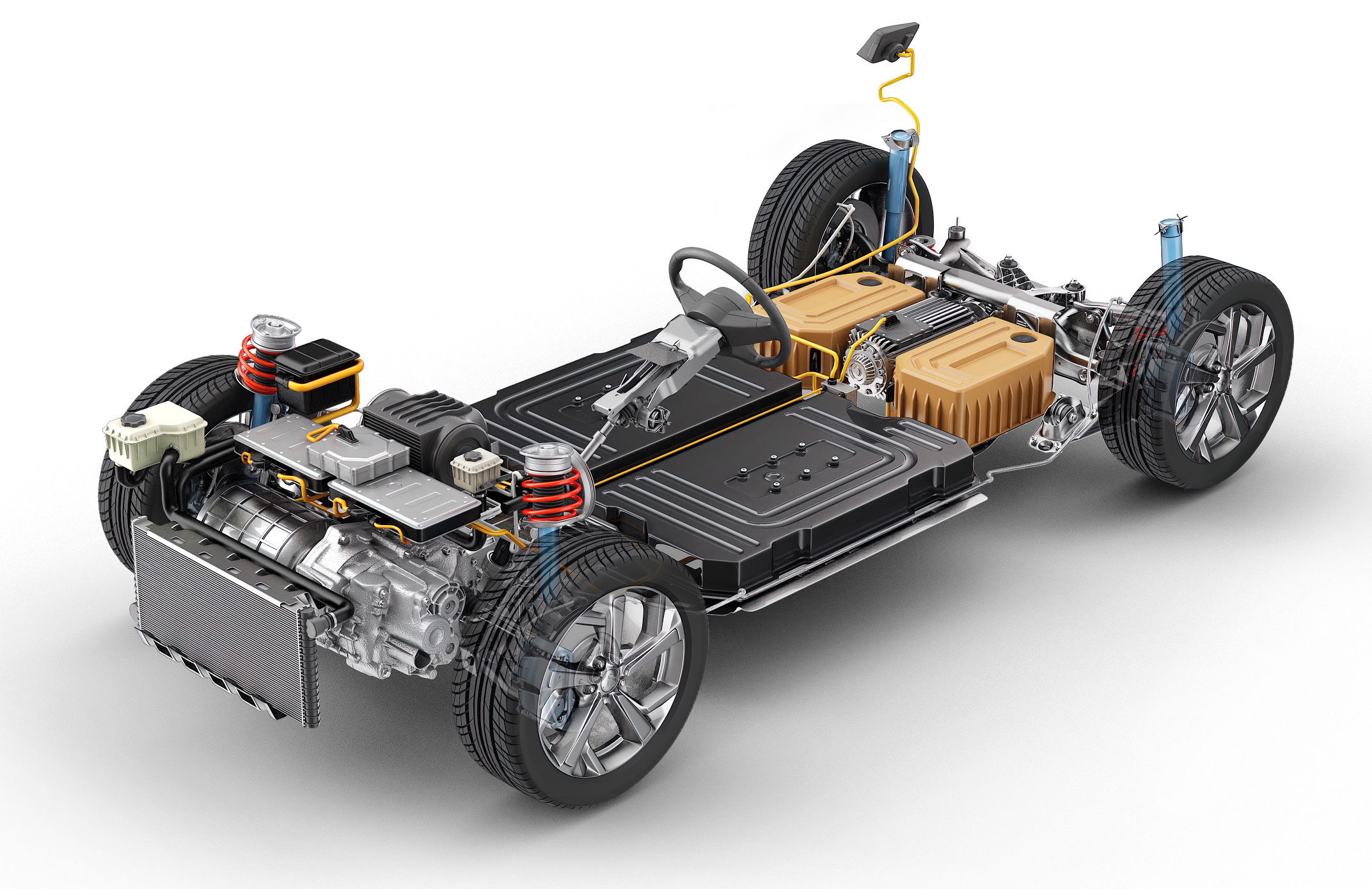
An electric vehicle (EV) is a type of vehicle that uses one or more electric motors for propulsion, rather than an internal combustion engine (ICE) that runs on fossil fuels. Electric vehicles are powered by electricity stored in rechargeable batteries or other energy storage devices, such as fuel cells.
There are several types of electric vehicles:
Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV): A battery electric vehicle is powered solely by electricity stored in rechargeable batteries. BEVs do not have an internal combustion engine and produce zero tailpipe emissions. They must be plugged into an external power source, such as a charging station or outlet, to recharge their batteries.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV): A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle is equipped with both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, along with a larger battery pack. PHEVs can operate in electric-only mode for a limited range, relying on the battery, and then switch to the internal combustion engine for longer trips. They can be charged from an external power source or by the internal combustion engine (through regenerative braking or while driving).


Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV): A hybrid electric vehicle combines an internal combustion engine with an electric motor and a small battery pack. Unlike PHEVs, HEVs cannot be plugged in to charge the battery; instead, the battery is charged through regenerative braking and while the vehicle is running. HEVs are designed to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions by supplementing the internal combustion engine with electric power.
As the automotive industry transitions towards electrification, electric vehicles are becoming increasingly popular as a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuel-powered vehicles. Governments around the world are also implementing policies and incentives to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles as part of efforts to combat climate change and improve air quality.